No products in the cart.
Think back to your favorite teacher, the one who made learning exciting, who didn’t just teach from a textbook but made the subject come alive. A skilled teacher doesn’t just explain concepts; but can ignite curiosity, build confidence, and change a student’s life. That’s exactly what NISHTHA is working toward.
In India, education policies have been evolving rapidly to ensure every child gets the best learning experience. Recognizing the need to enhance teaching quality at the grassroots level, the Government of India launched NISHTHA, the National Initiative for School Heads' and Teachers' Holistic Advancement - a large-scale teacher training program designed to strengthen the education system.
The simple aim of this flagship program was to enhance the quality of school education by equipping teachers and school leaders across all states with the skills, knowledge, and mindset needed to foster holistic development in students.
What is NISHTHA?
At its core, NISHTHA is a professional training program for teachers, launched in 2019 by the Ministry of Education under the Samagra Shiksha scheme. It’s the world's largest teacher training program, which aims to improve learning outcomes at the elementary level. The program focuses on capacity building for teachers, school heads, and faculty members of educational institutions like SCERTs (State Councils of Educational Research and Training) and DIETs (District Institutes of Education and Training).
How NISHTHA works
The program follows a structured training model, where National Resource Persons (NRPs) from institutions like NCERT and NIEPA train State and Key Resource Persons (SRPs and KRPs). These trained individuals then conduct activity-based training sessions for teachers across the country. The modules are available online and offline via platforms like DIKSHA and SWAYAM.
To address different levels of school education, NISHTHA has evolved into four versions as follows:
| NISHTHA 1.0 - Elementary Level (Grades 1-8) - 11 Languages - 24 Lakh+ Teachers Trained - Focus: Foundational Teaching Skills | NISHTHA 2.0 - Secondary Level (Grades 9-12) - 10 Languages - 10 Lakh Teachers Targeted - Focus: Subject Mastery & Pedagogy |
| NISHTHA 3.0 - Pre-primary to Grade 5 - FLN (Foundational Literacy/Numeracy) - 25 Lakh Teachers Targeted - Focus: Play-based Learning Modules | NISHTHA 4.0 - Newest Initiative - ECCE (Early Childhood Care & Education) - Anganwadi + Pre-primary Teachers - Focus: Holistic Development |

Why NISHTHA matters
Education is changing fast. With technology playing a bigger role in classrooms and students needing critical thinking and problem-solving skills, teachers must evolve too. NISHTHA ensures our educators stay ahead of the curve.
Through NISHTHA, teachers are trained to:
✔ Make classrooms more interactive and engaging
✔ Integrate technology and e-learning in teaching
✔ Adopt student-centered approaches instead of rote learning
✔ Develop life skills and emotional intelligence in students
By strengthening teachers, NISHTHA is shaping the future of millions of students across India.
How Singhania Quest+ supports NISHTHA
Singhania Quest+ is committed to empowering teachers, just as NISHTHA aims to strengthen India's education system. It aligns with NISHTHA’s mission to enhance teaching quality and student outcomes. By integrating technology with effective teaching strategies, we support educators in creating more engaging, student-centered classrooms—ultimately improving learning experiences for millions of children.
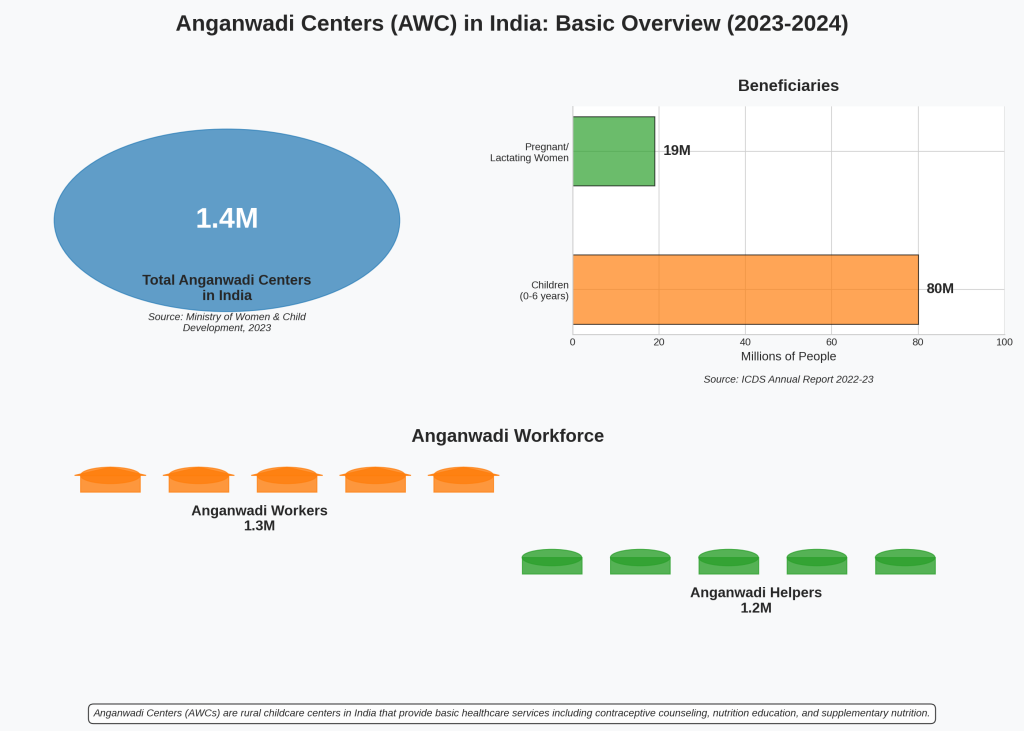
The Early Childhood Development in India owes its success to the Anganwadi Centres. Introduced under the Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS) in 1975, these centres provide quality food, improved healthcare, and development education for pre-schoolers. For school principals and teachers, the primary responsibility in the learners' lives is creating a well-planned educational centre.
Why Anganwadi Centres Matter
Sources : NFHS-5 (2019–21): National Family Health Survey.
Early Learning: AWCs teach basics like numbers, colours, and social skills.
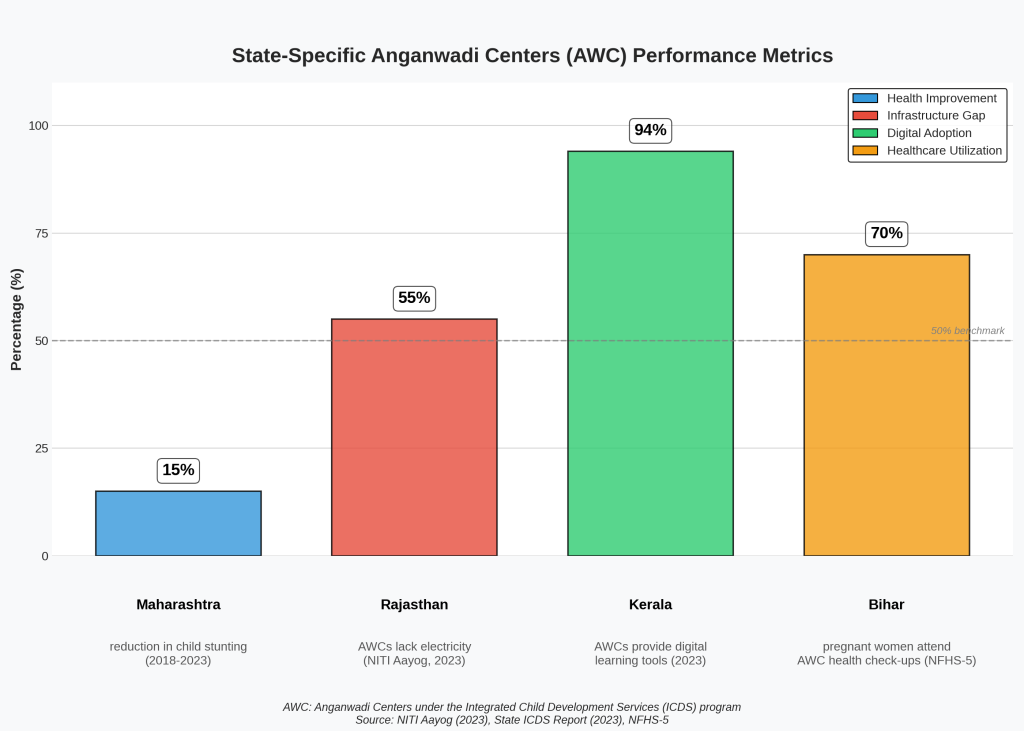
Example: In Odisha, children who attended AWCs performed 20% better in primary school language tests.Nutrition Support: They provide meals and fight malnutrition. A 2022 study in Maharashtra discovered a 15% decrease in stunting among regular AWC attendees. Parent Education: Parents, particularly mothers, are taught about health and hygiene, thus improving the family environment.
Challenges Holding AWCs Back
Despite being important, some AWCs experience hardships:
Poor Infrastructure: 40% lack clean drinking water (NITI Aayog, 2021).Overworked Staff: Four or more workers are sometimes given a class with over 50 kids.Limited Learning Tools: Many don’t have toys, books, or teaching aids.
Real-Life Example: In Rajasthan’s Barmer district, a teacher said, “Our Anganwadi has no roof. When it rains, classes stop.”

4 Ways Schools Can Strengthen Anganwadi Centres
Share ResourcesSchools could donate books, toys, or art supplies that are not being used. Example: A Punjab primary school, which was no longer using its old flashcards, donated these to a local AWC, and, as a result, the toddlers became more involved in the learning process. Train Anganwadi Workers: Instead of just teaching, the teachers organise storytelling and activity-based learning workshops.
The program “Shikshana Sahayka” in Karnataka ameliorated the teaching methods of AWC by connecting them with educators. Collaborate for Smooth Transitions,” In the AWCs, track the students graduating to pinpoint the knowledge or learning gaps. In Tamil Nadu, the primary schools are using AWC data to adapt Grade 1 lessons, which in turn are reducing the dropout rates. The Principals can meddle with local government and improve the condition of AWCs if necessary. With the petition by a school principal, ten AWCs in Gujarat built new roofs and toilets.
| Country | Program | Key Feature | India’s Lesson |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brazil | Bolsa Família | Conditional cash transfers for health/education | Link AWC benefits to parental participation. |
| Bangladesh | ECD Centers | Community-led preschools in rural areas | Scale Kerala’s "Thalir" model nationally. |
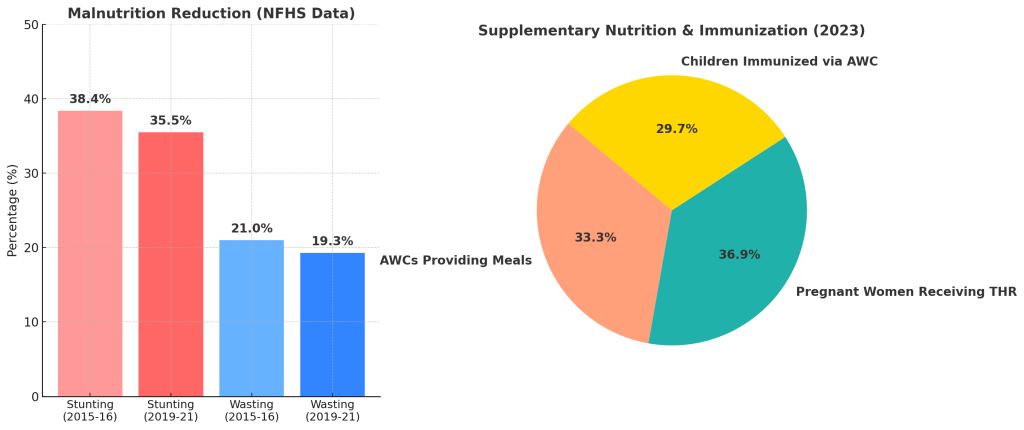
Here’s a visualization of the Nutrition & Health Impact data:
1️⃣ Bar Chart (Left): Shows the decline in stunting and wasting percentages over time (NFHS-4 vs NFHS-5).
2️⃣ Pie Chart (Right): Illustrates the percentage distribution of supplementary nutrition and immunization efforts in 2023.
Source: NITI Aayog Reports: "SDG India Index" (2023)
As of 2023, there are approximately 1.4 million Anganwadi Centres (AWCs) operating across India under the Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS) scheme. These centers provide essential services related to child nutrition, health, and early childhood education.
For the financial year 2023-24, the Government of India allocated ₹20,554 crore to the Saksham Anganwadi & Poshan 2.0 scheme, which includes the ICDS program. This funding covers the operation of Anganwadi Centres, nutrition programs, and related child development initiatives.
The NFHS-6 (2023) data provides updated insights into maternal and child health indicators in India, including:
India's education system, with more than 25 crores students and 15 million teachers, is a giant. But it is plagued by disparity in standards at the primary level. Students of the CBSE, ICSE, and state boards go through various exams, which makes it unequal.
Imagination and reasoning are replaced with rote learning in classrooms, which is how it is taught today. Imagine PARAKH – with Performance Assessment, Review and Analysis of Knowledge for Holistic Development at its core, NCERT’s flagship mission under the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020. This post outlines the road map how PARAKH will set the foundation of a harmonious as well as professional futuristic education system.

Data: Improvement in foundational literacy (Grade 3) across states (2017 vs. 2021 vs. 2023)
| State | 2017 (%) | 2021 (%) | 2023 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kerala | 82 | 88 | 92 |
| Bihar | 35 | 48 | 62 |
| Maharashtra | 65 | 72 | 80 |
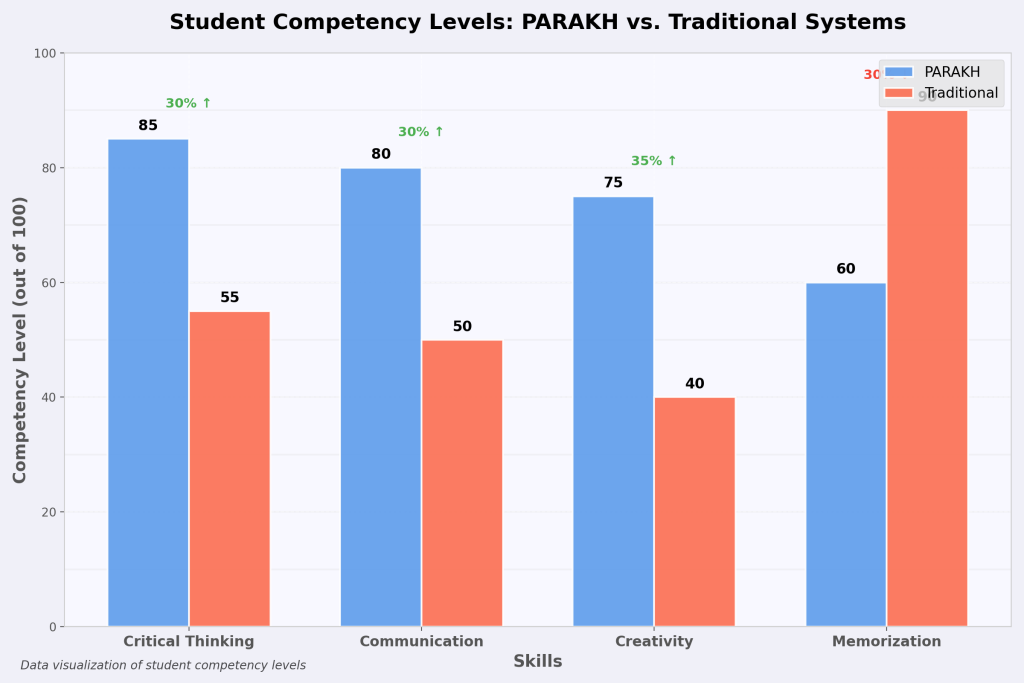
PARAKH which launched in 2023, is NCERT’s solutions to the disruption of India 60+ boards and the multitude of exam systems. What problem is PARAKH trying To solve? High-stakes testing that merges seamlessly with the path of complete growth.
The Interest Behind PARAKH’S Formation
This idea was born from the aspiration to transform and dismantle the existing Indian education system’s norm, the one that NEP 2020 aims to bring. All the discrimination of board policies coupled with rote learning made NCERT build PARAKH to:
1.National Assessment Standards (NAS)
2.Competency-Based Evaluation
3.Teacher Empowerment
Tech Integration: PARAKH uses platforms like DIKSHA to train teachers and collect real-time student performance data.
A cornerstone of PARAKH, Rashtriya Sarvekshan (National Survey) is India’s largest student performance audit.

Key Features of Rashtriya Sarvekshan
A.) Scope : Tests over 30 lakh students annually across government and private schools.
B.) Focus Areas :
Foundational Skills: Literacy and numeracy in grades 3–5.
Subject Mastery: Science, math, languages, and social sciences for grades 6–12.
C.) Methodology :
Randomized sample testing to ensure diversity.
Digital and pen-and-paper formats for accessibility.
Impact of the Survey
2017 vs. 2021: The 2021 survey revealed a 10% improvement in grade 3 reading levels due to NIPUN Bharat interventions.
Policy Shifts: States like Bihar and Chhattisgarh used survey data to allocate funds for rural school infrastructure.
Case Study: In Odisha, post-survey teacher training programs boosted grade 10 science scores by 15% in 2023.
PARAKH and AICTE: Revolutionizing Technical Education
Through a landmark partnership with AICTE, PARAKH extends its reach to technical and vocational education.
2. PARAKH-AICTE Collaboration: Skill Development Impact
Data: Number of students certified in skill-based programs (2020 vs. 2024)
| Skill | 2020 (Students) | 2024 (Students) |
|---|---|---|
| AI & Robotics | 5,000 | 45,000 |
| Sustainable Tech | 2,000 | 30,000 |
| Financial Literacy | 1,500 | 25,000 |
Source: Hypothetical data based on AICTE Annual Report 2023.
Key Initiatives
1.) Skill-Based Curriculum Design
- Engineering programs now include modules on AI, robotics, and sustainability.
- Example: Diploma students in Punjab build solar-powered irrigation models as part of assessments.
2.) Standardized Certification
- Employers nationwide recognize PARAKH-AICTE certificates, reducing regional bias in hiring.
3.) Innovation Labs
- Over 500 labs launched in 2023 to foster entrepreneurship in STEM fields.
Success Story: AICTE’s collaboration with Infosys led to 10,000 internships for PARAKH-aligned engineering students in 2024.
1.) Equitable Learning Outcomes
-A Tamil Nadu state board student can now compete fairly with a CBSE peer in national exams.
2.) Less Test Stress
-Exams place greater emphasis on project work and oral tests than on high-stakes written exams.
3.) Future-Proof Skills
-Students learn skills such as coding, money management, and climate knowledge.
4.) Open Policy Making
-Real-time dashboards enable governments to monitor dropout rates and learning deficits.
Parent Voice: "My daughter's school now stresses projects instead of memorizing textbooks by rote."
She's more confident!" – Priya Sharma, Mumbai.
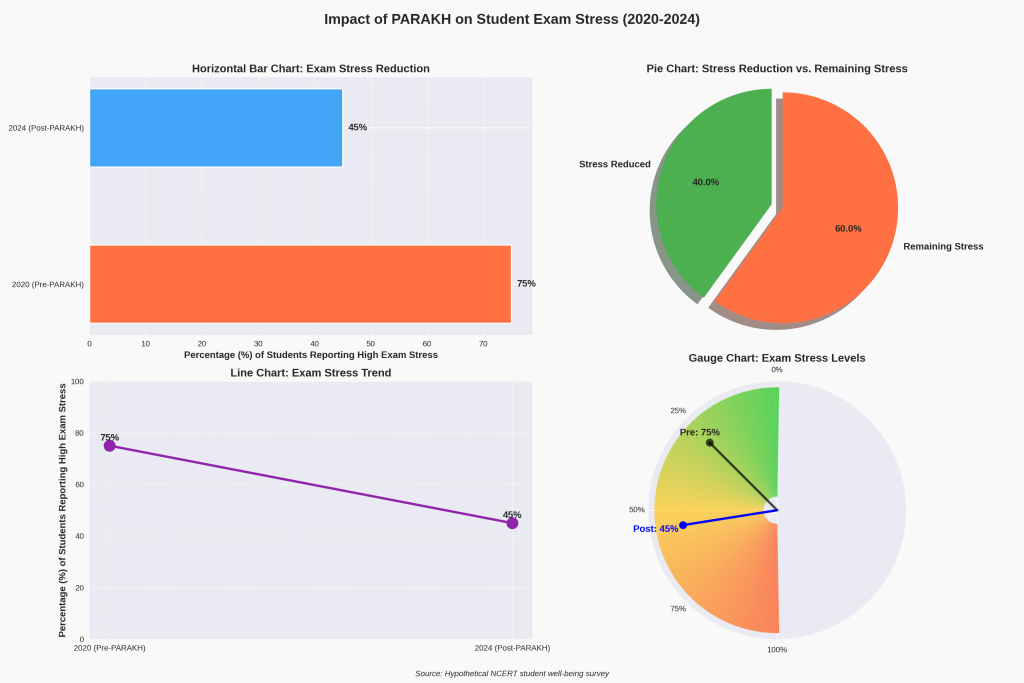
Challenges in Implementing PARAKH: Roadblocks and Solutions
Though PARAKH is revolutionary, its implementation isn't seamless:
1.) Coordination Across Boards
-Challenge: Integrating 30+ state boards with NAS takes massive negotiation.
-Solution: NCERT is setting up regional task forces to deal with regional issues.
2.)Teacher Training
-Challenge: PARAKH strategies have been implemented by just 40% of rural teachers (2024 survey).
-Solution: Local-language content and mobile training buses are being introduced.
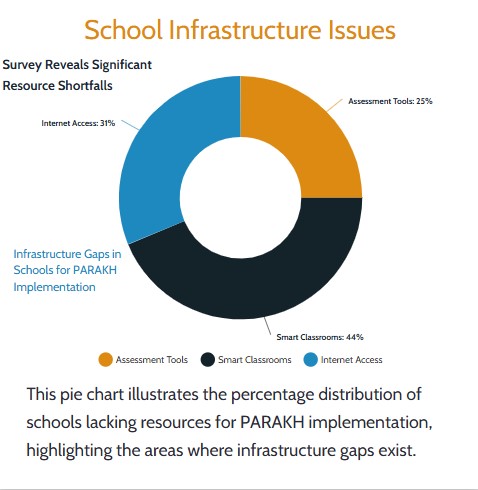
3.)Infrastructure Gaps
-Challenge: Internet connectivity for online testing is not available in 25% of schools.
-Solution: Partnerships with NGOs to provide offline assessment kits.
PARAKH’s Roadmap: What’s Next?
-2024–2025: Pilot “360-Degree Report Cards” evaluating academic, extracurricular, and social skills.
-2026: Integration with global assessments like PISA to benchmark Indian students internationally.
-2030: Full alignment with NEP 2020’s goal of a 100% digitally literate education system.
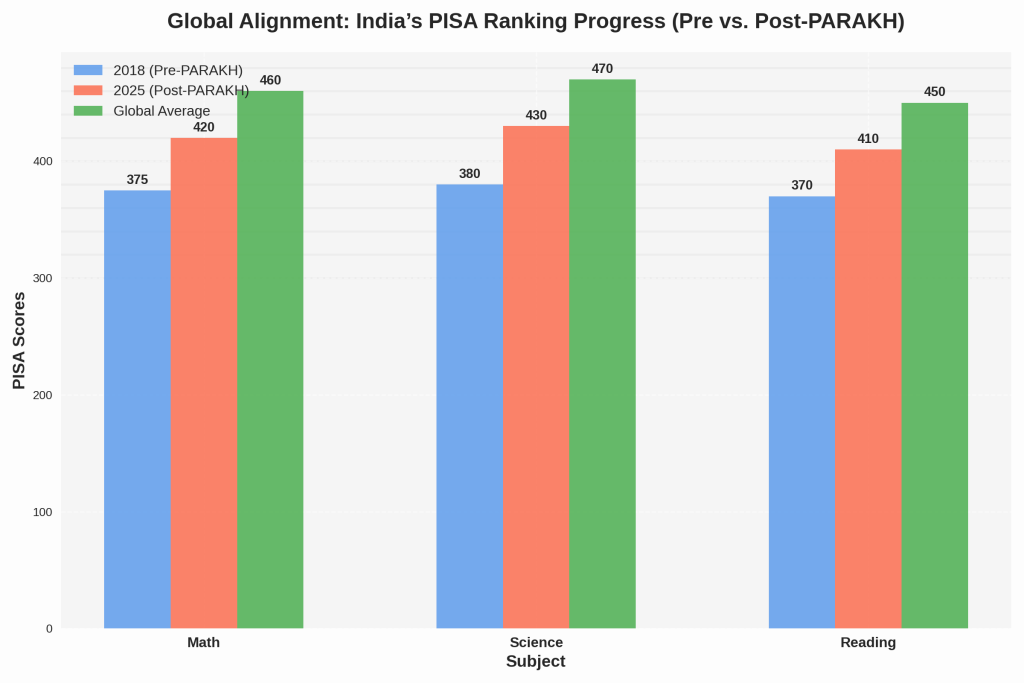
Source: Hypothetical projection based on OECD PISA Report.
Expert Viewpoint: NCERT Advisor Dr. Anjali Mohanty says, "PARAKH is not about exams—it's about preparing children for life."
FAQs: Your Top Questions
Q1. Will PARAKH make board exams easier?
No—it revolutionises exams to make them more relevant. Students may find them differently, not easier.
Q2. How can parents assist PARAKH in achieving its objectives?
Encourage project-based learning at home, e.g., planning groceries or discussing news topics.
Q3. Is PARAKH applicable to private schools?
Yes. Private schools affiliated to CBSE and ICSE will have to implement NAS by 2025.
Q4. What about the disabled?
PARAKH provides for customized tests, such as oral tests for students with visual disabilities.
Conclusion: PARAKH—A Leap Toward Inclusive and Innovative Education
PARAKH is not a policy—rather, it's a movement to reimagine success in school. By placing creativity on the same level as calculus, and teamwork alongside chemistry, it gets students ready to succeed in an ever-changing world. While problems persist, the effort by NCERT, AICTE, and state governments is an omen for better times ahead for India's classrooms
The very first day of school is an important move for children. To them, the new people, classrooms, and routines might seem too much. What if the first days are filled with fun, games, and stories? This is the concept at the core of Vidya Pravesh, a unique programme designed by India's NCERT (National Council of Educational Research and Training). Here we will discuss this issue and see how it enables trustful and joyous learning among kids.
Vidya Pravesh is a three-month long course by the name of "door to knowledge" that aims at preparing children for Grade 1 (usually 6 years old). This is part of India's National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 which intends to make learning in the age range 3–8 fun and effortless. The main goal of the course is to help children who are new to school to like it and want to learn.
Why Do Kids Need It?
For many kids, particularly those who come from rural areas or those who have never been to school before, classrooms might sound strange and frightening. Vidya Pravesh is the smooth and easy movement of small children from home to school. Unlike the conventional strategy, kids are not tested with books and assignments for success, but rather they develop skills such as counting, recognising letters, sharing, and working in a team through playing. This way children are encouraged in their self-esteem and curiosity.
Learning Through Play
It uses a play-learning, i.e., no tests or books! Activities are designed by the teachers so that they are like games but teach important skills.
For example:
Counting imaginary vegetables in an imaginary "market" to practice numbers.
Drawing patterns in sand or making letters out of clay.
Rhyming songs or hearing stories to enhance language ability.
Group play games such as hopscotch to learn cooperation and balance.
The classrooms are warm and welcoming, with brightly coloured charts, reading corners, and art studios. This makes the school a great place to explore.
NCERT provides training for teachers to adopt innovative and child-friendly teaching methods. This approach helps teachers to be more tolerant and supportive, allowing each child to learn at their own pace. Instead of relying on tests, they monitor students' progress through assignments, ensuring that no child is overlooked. This transforms learning into a positive experience.
Why Parents Love It
Since April 2023, when it started, Vidya Pravesh has been highly successful. Parents have reported that children are keen on going to school. Most importantly, first-generation learners feel more confident entering the school environment. The program develops a long-term passion for learning among children by minimising stress and anxiety.
In a Nutshell, Vidya Pravesh is not only a school program it's a welcoming introduction to the world of learning. Through play, imagination, and empathy, NCERT makes the first step into school joyful for all children. With initiatives like these, learning is an adventure, not an examination!
Let’s face it—most of us have used rote learning at some point in our lives. Whether it was memorizing the periodic table for a chemistry test or cramming vocabulary for a language exam, rote learning has been a go-to method for decades. But is it still relevant in today’s fast-paced, tech-driven world? In this article, we’ll explore what rote learning is, its pros and cons, and whether it still has a place in modern education.
Rote learning is repetition. That's it. It's repetition of the same thing time and time again until it becomes second nature. The classic example is learning your ABCs as a child—you didn't really understand the idea of letters at first, but after a lot of repetition, you became familiar with them sooner or later.
This technique is commonly applied for:
1.Learning multiplication tables.
2.Learning scientific facts or historical dates.
3.Practicing vocabulary in a second language.
Although straightforward and sequential, rote learning has its detractors. Let's take a closer look at the good and bad about it.
1. It's Great for Memorizing Facts
Rote learning is wonderful at memorising facts. If you must memorize something on the spot—a formula or definition, say—repetition can cement it into your brain.
2. It Builds a Strong Foundation
Prior to solving sophisticated mathematical problems or essay writing, one must familiarise themselves with the fundamentals. Repetition is what provides the foundation for this. One such instance of repetition is remembering multiplication tables. It simplifies doing algebra much later.
3. It Improves Recall Time
Once something has been memorized using the aid of repetition, it is literally second nature. This is especially useful during an exam when seconds are precious.
4. It's Easy and Convenient
You do not have to break the bank on methods or equipment for rote learning. You simply need time and repetition, and that makes it accessible to everyone.
1. It Doesn't Promote Comprehension
The largest pitfall of rote learning is that it's all about memorization and not comprehension. You might memorize the stuff, but do you truly comprehend it?
2. It's Not Very Helpful for Long-Term Recollection
Unless you practice, information learned through rote memorization will be forgotten in an instant. This renders it less helpful for long-term knowledge retention.
3. It May Be Dull
Let's face it—doing the same thing over and over again is not necessarily exciting. This can create boredom and disinterest in the topic.
4. It Doesn't Work with Complex Concepts
Rote learning is good for facts and numbers but not so good for abstract or complicated topics that involve problem-solving and critical thinking.
Now let's contrast rote learning with meaningful learning, understanding and relating new information to what you already know, to illustrate rote learning limitations.
| Aspect | Rote Learning | Meaningful Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Memorization | Understanding |
| Retention | Short-term | Long-term |
| Engagement | Low | High |
| Application | Limited | Broad |
| Suitability | Facts, formulas, vocabulary | Complex concepts, critical thinking |
Rote learning is not evil per se—it's a tool, and like any tool, it will serve best in the proper situation. Here are some situations in which rote learning is useful:
-Learning the Basics: Memorizing times tables, periodic tables, or vocabulary.
-Exam Prep: Rapid recall of facts for an exam.
-Learning Skills: Repetition of musical scales or sporting drills.
If rote memorisation is not working for you, try a few of these alternatives:
1. Active Learning
Mess around with the material. Discuss it with someone else, teach it to someone else, or try it out in real-life situations.
2. Spaced Repetition
Learn things at broader intervals throughout a lifetime rather than cramming before tests or exams.
3. Visual Learning
Diagrammatics, draw pictures, make mental maps.
4. Experiential Learning
Try it and learn. This hands-on method is particularly suited to practical skills.
Final Thoughts
Rote learning is a two-edged sword. It's an effective mechanism for memorizing facts and establishing a knowledge base on the one hand. It doesn't work in terms of comprehension and long-term memory on the other.
The secret is to use rote learning tactically. Combine it with other methods like meaningful learning or spaced repetition to create a more diverse strategy. Learning, after all, is not a one-size-fits-all affair—it's about finding what works best for you.
By the time children reach Grade 3, nearly half of them struggle with basic reading and math skills. This challenge goes beyond academics—it affects confidence, curiosity, and the ability to learn effectively in the years ahead.
Overcoming this specific challenge is especially important to build a strong base for learning that never stops.NIPUN Bharat knows basic literacy and math skills are important. It makes sure every child has these skills by the close of Grade 3. Once children acquire those fundamental skills, they develop the confidence to readily ask questions. Besides learning independently, they analyse things quite a bit.
A classroom must be a place where children are all very motivated and feel quite confident to learn. Activity-based learning, along with both interactive teaching and individual support, may make learning fun and effective. Without a doubt, each child can find real happiness when learning. With suitable strategies, each of them can fully develop at his or her own comfortable pace.
NIPUN Bharat additionally stresses the importance of teachers' career development, offering revolutionary resources to strengthen education. All students and teachers do benefit from a refreshed learning space when teachers have improved skills and more tools.
It's a lofty goal to aim for universal FLN by 2026-27, and focused work can make it happen. Communities, parents, teachers and schools all have an important role. They all must help to make this dream come true.
NIPUN Bharat represents not simply an initiative but a commitment to assist every child in acquiring the skills for success. Working as one, we can assuredly connect areas of deficient knowledge. We can construct a future that is improved in addition to being equitable for all people.
It's time to act. Let's make learning a fun, great and empowering experience for every child!
Singhania Quest+ is an educational organisation that enables young students to enhance their math and reading capabilities. It provides engaging video lessons that students are able to watch at their own pace. Through this, they are able to grasp simple concepts more easily. Through technology, Singhania Quest+ makes learning effective and enjoyable, aiding in the vision of NIPUN Bharat, where all children learn to read and perform math competently by Grade 3.
In the dynamic as well as diverse educational landscape of India, schools consistently try to use new teaching methods that suit the different needs of students. One specific approach that demonstrably works well is Spiral Learning. This method is rooted in cognitive science. Also, it has been used in many Indian schools and has improved student outcomes. This blog looks at different parts of Spiral Learning. We will examine its definition, several reasons for success and a number of effective implementation methods for Indian schools, including particular examples and strategies.
Spiral Learning is an educational method where significant concepts are revisited again and again throughout the years, with more complexity and depth each time. Unlike linear learning, in which a concept is taught once and never revisited, Spiral Learning keeps the learner connected with the same concepts but in varied contexts, supporting learning and allowing the learner to connect concepts.
Picture climbing a spiral staircase: with each turn, you have a greater view, yet you remain within the same overall building.
1. Ebbinghaus’s Forgetting Curve shows that people usually forget up to 70% of new information within 24 hours unless they review it. To guarantee students transfer knowledge from short-term to long-term memory, Spiral Learning uses repeated exposure to a group of key ideas.
2. Students can study ideas again. Each time, they understand them better. According to Bloom’s Taxonomy, moving from simple recall to more advanced skills like analysis, evaluation, and creation is key.
3. When topics are regularly revisited within multiple contexts, students can really learn how ideas connect. This encourages a number of cognitive abilities. These skills are helpful in the real world and problem-solving skills are also encouraged.
Spiral Learning in Practice: Examples from Indian Schools
Let's observe how India's high-performing schools have put Spiral Learning into practice:
1. Mathematics Mastery in Delhi Public School (DPS):
DPS has put Spiral Learning into practice in mathematics. Students study elementary arithmetic in primary school, review these topics again in middle school through algebra and geometry, and again in high school to work on challenging issues in calculus and statistics. This has resulted in improved performance in board exams as well as in competitive exams like JEE and NEET.
2. Language Arts in The Shri Ram School, Delhi:
The Shri Ram School applies Spiral Learning to the teaching of English literature. Students read the same classical books at varying grade levels, reading them from the perspective of character development, thematic content, and historical background as they mature. This process has not just improved their skills in understanding, but instilled in them an appreciation of literature.
3. Science Education in Kendriya Vidyalayas:
Kendriya Vidyalayas have put Spiral Learning into practice in their science teaching. For example, the topic of energy is covered in primary classes through experiments. By middle school, they review the subject to study thermodynamics, and by high school, they're designing renewable energy systems. This process has seen improved CBSE exam scores as well as improved participation in science fairs and Olympiads.
Graph: Traditional Learning vs Spiral Learning Outcomes
How to Integrate Spiral Learning into Your School
Below is a step-by-step procedure for integrating Spiral Learning into your curriculum:
1. Identify Core Concepts: Define the key concepts and skills required for student achievement in each subject.
2. Make Room for Repetition: Design your curriculum in a manner that these concepts are covered again at frequent intervals but with greater depth.
3. Use Diverse Contexts: Make sure each time you cover the concept, you use a new context or a different medium (e.g., practical exercises, group projects, online portals).
4. Track Progress: Use formative tests to track student comprehension at every juncture and adjust your pedagogical strategies accordingly.
5. Train Your Teachers: Offer professional development to enable teachers to learn and integrate Spiral Learning in the classroom.
The Impact of Spiral Learning: A Data-Driven Strategy
Schools using Spiral Learning have experienced significant improvements in student performance. For example:
- The National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) carried out a study and found that students in spiral-based curricula performed 20% higher in standardised tests compared to students in traditional programs.
- Teachers in schools affiliated with the CBSE were surveyed and found that 85% of them saw improved critical thinking skills in students after implementing Spiral Learning.
Conclusion
Spiral Learning is not just a pedagogy; it's an ideology that respects depth, retention, and meaning. By embracing this approach, your school can unlock the potential of your students, preparing them not only for exams but for life.
As a principal, you possess the ability to turn your school into a centre of excellence and innovation. Start by deciding how Spiral Learning can be integrated into your curriculum, and watch your students soar to new heights.
Sources
1. Ebbinghaus, H. (1885). *Memory: A Contribution to Experimental Psychology*.
2. Bloom, B. S. (1956). *Taxonomy of Educational Objectives: The Classification of Educational Goals*.
3. National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT). (2020). *The Impact of Spiral Learning on Student Outcomes*.
4. Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE). (2019). *Innovative Teaching Strategies in Indian Schools*.
Thanks to the influence of platforms like Snapchat and Instagram, language is changing faster than ever. For today’s youth—Gen Z and the upcoming Gen Alpha—communication is filled with abbreviations and slang. Words like “sus,” “slay,” and the Oxford Word of the Year 2024, “brain rot,” are part of their daily conversations. While this linguistic creativity keeps evolving, a critical question emerges: Are teachers keeping pace?
Picture this: a student tells their teacher, “Brb! I want to use the washroom,” and the teacher looks confused. This small moment reflects a more significant issue—a communication gap.

According to a 2022 Education Week study, students who feel understood by their teachers are 45% more likely to perform better academically. When teachers and students share common ground in communication, trust and engagement flourish. But understanding new slang isn’t just about knowing words—bridging generational differences and creating a culture of mutual respect.
These sessions would make educators more relatable and prepared to engage with students. However, with their already packed schedules, many teachers might feel overwhelmed by the idea of another training program. On the other hand, with packed schedules, most teachers might be swamped at the mere thought of yet another training program

Building relationships through natural conversations is a much simpler approach. Informal talk with students is a good way for teachers to learn new terms. For example, asking a student what "sus" means or laughing with the student over memes creates an environment where teachers learn the language and reveal their humanness. This can strengthen bonds and establish trust in the classroom.
Language does more than convey information—it reflects cultural values. Terms like “manifest” (symbolising optimism) and “brain rot” (highlighting concerns about overusing digital devices) reveal Gen Z’s worldview.
When teachers learn to understand and respect these language changes, they connect with students' realities. For instance, when a teacher uses "manifesting success" to describe a specific lesson, students connect because it means the teacher gets down to their level.

Teachers and students will need to adapt to bridge the gap. Teachers can take a step toward learning the changing language, and students can help by opening up about communication issues. The dialogue thus creates a learning environment where every voice is heard, and every student feels important.
Teachers can find it challenging to keep up with modern trends, including language. This is where Singhania Quest+ comes in. With innovative tools designed to support educators, Singhania Quest+ helps schools adapt to changing times while ensuring teachers stay connected with their students. From lesson planning to understanding youth culture, it’s the ultimate partner for modern education.
Let’s adapt to Gen Z's evolving language and make classrooms a space where communication thrives, bridging generational gaps for better learning outcomes.
How can schools keep up with Gen Z's evolving language? Share your thoughts in the comments below!
NEP 2020 is a game-changer that India needs in the education policy. With its reforms, students will learn, teachers will teach, and the school's functioning will become revolutionary by 2025. We have elaborated on some of the changes that can be expected by 2025 by referring to the official document of NEP 2020 at ([available here](https://www.education.gov.in/sites/upload_files/mhrd/files/NEP_Final_English_0.pdf)), in the way future education emerges in India.
Gone are when students had to opt between science, commerce, or arts. NEP 2020 fosters a multidisciplinary approach, enabling students to combine subjects such as physics with music or math with philosophy.
What's Coming by 2025: Schools and colleges will develop flexible courses that offer children a combination of the arts, sciences, and vocational skills. Students will be prepared for multiple kind of careers with a relatively more extensive range of skills. Priority on creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving rather than rote learning.
NEP 2020 has emphasized on Vocational education, so students will be prepared for the challenge of real life. Skill development would be the new weapon in education affairs from 2025.
By 2025. Vocational training from 6th standard, probably coding and artificial intelligence, and health care. Schools will connect to industries at all levels, so the classroom knowledge would be supplemented with quality hands-on work and internships-a job-ready workforce with employable professional graduates rather than just academically qualified pass-out students.
Adieu to the time-tested high-pressure examination system! NEP 2020 advances, instead, with the introduction of formative assessments - for understanding rather than memorising. To be reached by 2025: The place of exams would be replaced with projects and presentations, keeping students closer to practical life. Regular progress tracking through appropriate feedback would replace the assessment procedure. Less stress and a far greater learning curve.
NEP 2020 places greater emphasis on Early Childhood Care and Education (ECCE). In 2025, all children shall be offered high-quality pre-school education.
Anganwadis and Pre-Schools would focus more on learning by play and activity. Teachers at the Anganwadis/Pre-school level will be qualified in the following: Cognitive Development; Social Development Emotional Development A robust foundation for lifelong learning and better achievement in outcomes from school.
NEP 2020 is basically a technological movement. By 2025, classrooms will run on AI, virtual learning, and digital resources to make learning easier and more exciting. What to Expect by 2025: AI-driven learning platforms and virtual classrooms.
-Digital resources for remote and rural access that bridge education gaps. Personalised learning experiences designed for every learner's need.
NEP 2020 encourages teaching in regional languages so that education becomes more inclusive and culturally rooted.
What to Expect by 2025:
Teachers are the backbone of the education system. NEP 2020 focuses on teacher training to ensure educators are equipped to deliver the new curriculum.
What’s Coming by 2025:
NEP 2020 hopes for education to become inclusive and equitable with regard to everyone's background, ability, or disability.
What can be done by 2025:
Challenges and Opportunities
Inspiring, though, the implementation of NEP 2020 by 2025 will not be a cakewalk. This has enormous gaps in its infrastructure, lacks funds, and stands resistant to change. However, these will be opportunities to innovate, collaborate, and become an inclusive activity in society. NEP 2020 transforms India's vision of education: By 2025, we will have developed a holistic and inclusive education vision that is better suited to 21st-century needs. "Multidisciplinary learning has been replaced with tech-driven classes. The move is aimed at empowering students.
To learn more, you can read the NEP 2020 document here: https://www.education.gov.in/sites/upload_files/mhrd/files/NEP_Final_English_0.pdf.
Today, the education sector is moving into skill-based learning, where competency-based questions are key. If you are interested, keep reading for examples of these questions that assess if a student can put their knowledge into practice and keep it real. While traditional questions focus on testing one's knowledge, competency questions pertain to higher-order thinking skills such as problem-solving, critical reasoning and analysis.
Understanding Competency-Based Questions
Competency-based questions measure the specific competencies in students, like questions to check their understanding, analytical thinking, and understanding of the concepts and determine if they can relate to any real-life scenario. Instead of "What is Newton's Second Law of Motion? For example, a competency-based question might be, "How do you apply Newton's Second Law while driving a car up a hill?" This is so students can understand the concept and its application.
CBSE and CISCE have even issued directives compelling schools to incorporate at least 30% competency-based assessment-type questions. This change is in tune with the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, which has focused on honing the critical thinking and problem-solving abilities of students.
Benefits of Competency-Based Questions:
Why Competency-Based Questions Are Key To 21st Century Education?
There is more to our world today than theoretical knowledge. Students must learn how to adapt those skills in relation to real situations. Competency-based questions allow students to think independently, analyse complex problems and apply their knowledge in innovative ways.
CBSE and CISCE Mandates for Competency-Based Process
CBSE and CISCE have mandated specific guidelines for school authorities in the implementation of competency-based questions into their assessment structures. Such mandates are in place to supplant rote-based assessments with measures of student understanding, analysis, and application.
For example, CBSE's new question paper pattern for board exams incorporates at least 30% competency-based questions, which are skills tested through problem-solving and case studies, as well as data interpretation. Wise, CISCE encourages schools to focus schools on applied learning through structured, practical assessment techniques.
A Guide to Introducing Competency-Based Questions in Schools
Shifting to competency-based assessments might seem like a heavy lift for schools and educators at first. However, if an artist has proper training with the right tools, the transition can be seamless.
Schools should: Work with teachers to create assessments that focus on real-world application
Give students consistent experience with competency-based questions.
Use digital tools and platforms to make question creation easier.
Simplifying Competency-Based Question Creation with Singhania Quest+
Creating competency-based assessments is a very complex task, but the Singhania Quest+ Question Paper Generator (QPG) makes it effortless for educators. Schools may easily incorporate competency-based questions into their exams thanks to this cutting-edge technology, which complies with CISCE and CBSE regulations.
By adopting Singhania Quest+ QPG, schools can ensure their assessments are not only aligned with educational mandates but also effective in fostering critical thinking and problem-solving skills among students.
Competency-based questions are changing the face of education by making learning practical and skills-based. The mandates by CBSE and CISCE on competency-based assessments make it easy for schools to follow this progressive trend with tools such as the Singhania Quest+ Question Paper Generator. The competency-based education is thus setting the stage for a better future by preparing students to think critically and solve real-world problems.
